PyPNM - Pythonic Portable Any Map image files reading, displaying and writing
Introduction
PyPNM is a Python module for reading PPM and PGM image files (both 8 and 16 bits per channel color depth) to image 3D integer lists for further editing, displaying 3D lists obtained by converting to Tkinter-compatible data in memory, and subsequent writing edited image 3D lists to disk as PPM or PGM files, either binary or ASCII.
Portable Pixel Map (PPM) and Portable Gray Map (PGM) (particular cases of PNM format group) are simplest file formats for RGB and L images, correspondingly. In theory, you may import ASCII PGM even in Excel, turning Excel into image editor. Unfortunately, this simplicity lead to adverse consequences:
- lack of strict official specification. Instead, you may find words like "usual" in format description. Surely, there is always someone who implement this part of image format in unprohibited, yet a totally unusual way;
- unwillingness of many software developers to provide any good support for simple and open format. It took years for almighty Adobe Photoshop developers to include PNM module in distribution rather than count on third-party developers, and surely (see above) they took their chance to implement their own header scheme nobody else uses. What as to PNM support in Python, say, Pillow... sorry, I promised not to discuss Pillow anywhere ladies and children are allowed to read it.
As a result, novice Python user (like me) may find it difficult to get reliable input/output modules for PPM and PGM image formats; therefore current PyPNM package was developed, combining input/output functions for 8-bits and 16-bits per channel binary and ascii PGM and PPM files, i.e. P2, P5, P3 and P6 PNM file types. P1 and P4 (1 bit) PBM formats are supported only for reading.
PyPNM key functionality comprise:
- previewing image being edited by converting it into PNM-like byte structure to be displayed using Tkinter PhotoImage(data=...) method;
- reading PPM, PGM and PBM files from disk into image representation as 3D nested list;
- writing image representation as 3D nested list to PPM or PGM file on disk.
So, in general, main goal of PyPNM is to simplify writing image editing applications in Python, be it a prototype or a fully blown application.
(Interlude start) Actually what I needed was small and simple facility for displaying image-like data for image editing/filtering applications like «Averager». Yes, I want to be able to write image filter in Python and view result without huge extra packages, full of useless features for a price of lack of needed ones. Using Tkinter with PPM/PGM looked like simplest solution, so I created some module for turning nested 3D lists to PPM-like bytes structures in memory. Since it required learning PNM specs anyway, I decided to add PPM/PGM files reading and writing on top of that. Etc., as Kurt Vonnegut kept saying. (Interlude end)
You may easily acquire PyPNM module either from GitHub or from PyPI and use it absolutely free.
PyPNM version |
Download site |
Download content |
|---|---|---|
Current version |
PyPNM module and sample viewer application, |
|
Python 3.4 compatible |
PyPNM module and sample viewer application, |
|
PyPNM module only, for Python 3.4 and above. |
Recent updates
Update: PyPNM updated to version 2.26.22.34. Importing significantly simplified.
Previously on PyPNM: PyPNM updated to version 2 (3 Sep 2025 «Victory II»)
This major update includes numerous measures focused on reducing resource usage:
- using mmap instead of direct file reading;
- using generators instead of intermediate lists wherever possible.
Note that although module was completely rewritten, input and output types and data structure remain the same, so versions 2.21.3.* «Victory II» are completely interchangeable with 1.17.9.* «Victory».
In ver. 1.17.9.34 «Victory» (maximum compatibility) forced 8 bit preview for 16 bit images implemented when running under old Python versions (prior 3.11).
In ver. 1.17.1.1 PNM export functions restructured to provide easy format switch (binary⇄ASCII). Backward compatibility maintained.
In ver. 1.15.1.1 image viewing function updated to show LA and RGBA images over chessboard background (like Photoshop and GIMP). This mode requires enabling newly added option, which, in turn, requires you to 📘RTFM.
In ver. 1.14.8.19 memory usage for writing PPM and PGM files greatly reduced. Binary files (P6 and P5 correspondingly) are written per image row (which is considered as reasonable tradeoff between memory usage and disk thrashing); ASCII files (P3 and P2) are written per sample (which is minimal memory using scenario).
Format compatibility
Image format | File format | Read | Write |
|---|---|---|---|
16 bits per channel RGB | P6 Binary PPM | ✅ | ✅ |
16 bits per channel RGB | P3 ASCII PPM | ✅ | ✅ |
8 bits per channel RGB | P6 Binary PPM | ✅ | ✅ |
8 bits per channel RGB | P3 ASCII PPM | ✅ | ✅ |
16 bits per channel L | P5 Binary PGM | ✅ | ✅ |
16 bits per channel L | P2 ASCII PGM | ✅ | ✅ |
8 bits per channel L | P5 Binary PGM | ✅ | ✅ |
8 bits per channel L | P2 ASCII PGM | ✅ | ✅ |
1 bit ink on/off | P4 Binary PBM | ✅ | ❌ |
1 bit ink on/off | P1 ASCII PBM | ✅ | ❌ |
Image representation
Is seems logical to represent an RGB image as nested 3D structure - X, Y-sized matrix of three-component RGB vectors. Since in Python list seem to be about the only variant for mutable structures like that, it is suitable to represent image as (list(list(list(int)))) structure (for example, this structure was used for ScaleNx image resizer and Adaptive Average image filtering, and worked well). Therefore, it would be convenient to have module read/write image data from/to such a common structure.
Coordinate system of RGB image.
List index structure correspond to typical image coordinate system assumed for image editing software like Photoshop, GIMP, Paint Shop Pro etc, with [0, 0] origin at top left corner.
Note that for L images memory structure is still (list(list(list(int)))), with innermost list having only one component, thus enabling further image editing with the same nested Y, X, Z loop regardless of color mode. I understand that this may sound surprising for professional image I/O programmers, but for normal people writing a loop once and for all is a sort of expected behaviour.
Also, since this module is supposed to be used for image editing rather than just reading, when reading 1 bit PBM files into image this module promotes data to 8 bit L, inverting values and multiplying by 255, so that source 1 (ink on) is changed to 0 (black), and source 0 (ink off) is changed to 255 (white). For the same reason writing 1 bit PBM files is not planned - 1 bit images are next to useless for editing.
pnmlpnm.py
File pnmlpnm.py is a core of PyPNM and contains 100% pure Python implementation of everything one may need to read/write from/to a variety of PGM and PPM files. I/O functions are written as functions/procedures, as simple as possible, and listed below:
- pnm2list - reading binary or ascii RGB PPM or L PGM file and returning image data as ints and nested list;
- list2bin - getting image data as nested list of ints and creating binary PPM (P6) or PGM (P5) data structure in memory. Suitable for generating data to display with Tkinter;
- list2pnm - getting image data as nested list of ints and writing either binary or ASCII PNM image file, depending on "bin" switch.
- create_image - creating empty nested 3D list for image representation. Not used within this particular module but often needed by programs this module is supposed to be used with.
Functions arguments description is provided in docstrings, but in general looks as simple as that - you feed the function with your image data list and a filename, and get PNM file written; or you feed it to another function and get your image displayed.
More prolific description is available in PyPNM documentation bedside book (PDF) (📘PDF, 7 pages); or, if you hate well-orchestrated well-illustrated docs, just explore simple sample below:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from tkinter import Button, PhotoImage, Tk
from pypnm import pnmlpnm
X, Y, Z, maxcolors, image3D = pnmlpnm.pnm2list('example.ppm') # Open
pnmlpnm.list2pnmbin('binary.ppm', image3D, maxcolors) # Save as binary
pnmlpnm.list2pnmascii('ascii.ppm', image3D, maxcolors) # Save as ascii
main_window = Tk()
main_window.title('PyPNM demo')
preview_data = pnmlpnm.list2bin(image3D, maxcolors) # Generating preview bytes from list
preview = PhotoImage(data=preview_data) # Generating preview object from bytes
preview_button = Button(main_window, text='Example\n(click to exit)',
image=preview, compound='top', command=lambda: main_window.destroy())
preview_button.pack()
main_window.mainloop()
Yes, above is an illustration of all functions of PyPNM in action: opening file as image list, saving image list as binary file, saving image list as text file, showing image list as image with Tkinter. With addition of just some 10-12 kb of widgets and event handling it turns into a good-looking fully functional viewer and converter below.
Viewer.py
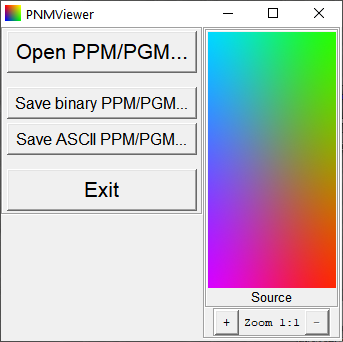
Program Viewer.py is a minimal (i.e., GUI is deliberately reduced to right-click menu, and stuff like Ctrl+click and Alt+click for zooming, familiar to Photoshop users) illustrative utility: using PyPNM package, it reads different flavours of PGM and PPM files, and allows saving them as different types of PGM/PPM, e.g. it can read ASCII PPM and write it as binary PPM or vs. Also this program shows image data using PyPNM and Tkinter. No, there is no mistake: it does not feed PPM files to Tkinter directly. Instead, it uses nested 3D list data loaded using PyPNM to generate in-memory bytes object of PNM structure using preview_data = pnmlpnm.list2bin(image3D, maxcolors), and then feeds this in-memory bytes object to Tkinter as preview = PhotoImage(data=preview_data) (note using data=, not file=). This way it shows formats which Tkinter itself cannot handle, like ASCII PNM (example of 16-bit ASCII PPM being displayed by simple viewer based on PyPNM is shown at the right).
Fun fact: Icon in Viewer.py is not the icon, but bytes of PPM produced with pnmlpnm.py and then hardcoded into viewer as byte string. It's 2x2 pixels of basic colors, so when rescaling Tkinter turns it into a four-point gradient (oh well, with Python 3.4 under Windows XP it uses nearest neighbour, so you see perfect squares of pure colors).
All this means that you may use PyPNM and Tkinter to visualize any data that can be represented as greyscale or RGB without huge external packages and writing files on disk; all you need is Tkinter, included into standard CPython distributions, and highly compatible pure Python pnmlpnm.py taking only 20 kbytes.
Now when you have initial understanding of what PyPNM module is and how it may be used to work with images in general and PGM and PPM files in particular, it's time to pull PyPNM from GitHub and start working with images yourself.
...or move back to Dnyarri`s Python freeware main page.